Getting started¶
Demonstration¶
The screencast below demonstrates how to install, configure and use PyQSO (focussing on version 1.0.0 only). Detailed instructions are also available in the sections that follow.
System requirements¶
It is recommended that users run PyQSO on the Linux operating system, since all development and testing of PyQSO takes place there.
As the name suggests, PyQSO is written primarily in the Python
programming language (version 3.x). The graphical user interface has been developed using
the GTK+ library through the PyGObject bindings. PyQSO also uses an
SQLite embedded database to manage all the contacts an amateur radio
operator makes. Users must therefore make sure that the Python
interpreter is installed and that any additional software dependencies are satisfied
before PyQSO can be run successfully. The list of software packages that
PyQSO depends on is provided in the README.md file.
Installation and running¶
Assuming that the current working directory is PyQSO’s base directory (the directory that the Makefile is in), PyQSO can be run without installation by issuing the following command in the terminal:
python3 bin/pyqso
If the pip3 package manager is available on your system then PyQSO can be installed system-wide using:
sudo make install
Once installed, the following command will run PyQSO:
pyqso
Command-line options¶
There are several options available when executing PyQSO from the command-line.
Open a specified logbook file¶
In addition to being able to open a new or existing logbook through the
graphical interface, users can also specify a logbook file to open at
the command line with the -l or --logbook option. For example, to
open a logbook file called mylogbook.db, use the following command:
pyqso --logbook /path/to/mylogbook.db
If the file does not already exist, PyQSO will create it.
Debugging mode¶
Running PyQSO with the -d or --debug flag enables the debugging
mode:
pyqso --debug
All debugging-related messages are written to a file called pyqso.debug,
located in the current working directory.
Creating and opening a logbook¶
A PyQSO-based logbook is essentially an SQL database. To create a new database/logbook file, click Create a New Logbook... in the Logbook menu, choose the directory where you want the file to be saved, and enter the file’s name (e.g. my_new_logbook.db). The new logbook will then be opened automatically. If you would like to open an existing logbook file, click Open an Existing Logbook... in the Logbook menu. Note that logbook files usually have a .db file extension.
Once the logbook has been opened, its name will appear in the status bar. All logs in the logbook will be opened automatically, and the interface will look something like the one shown in figure:logbook.
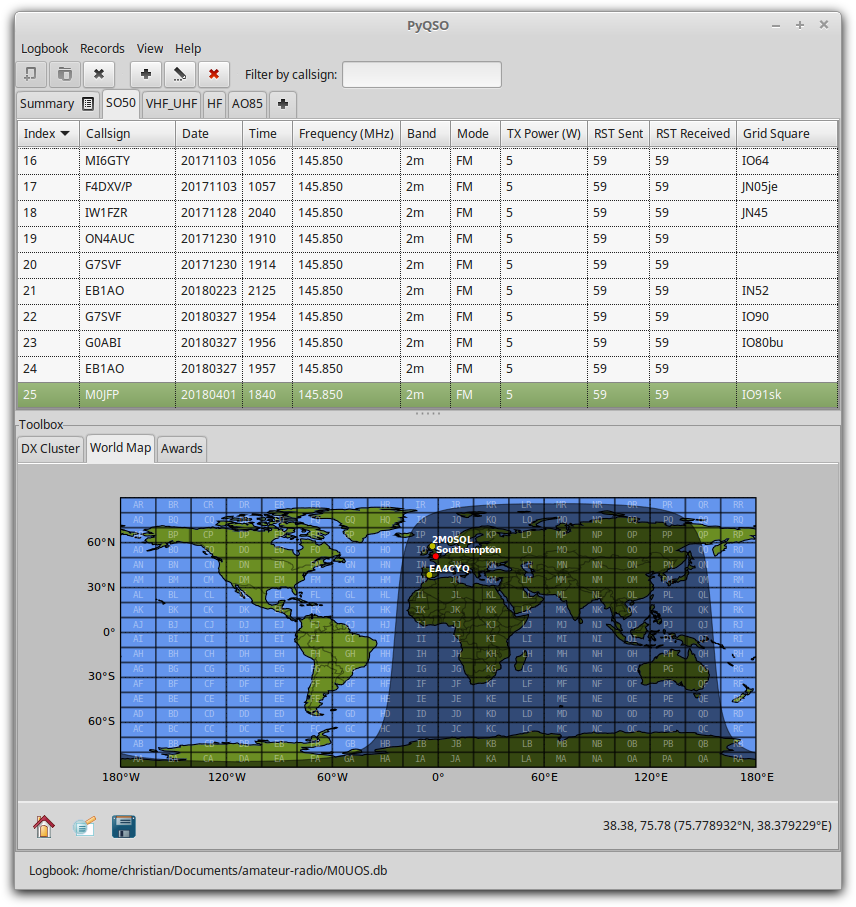
The PyQSO main window, showing the records in a log called
SO50(for contacts via the amateur radio satellite SO-50), and the World Map tool in the toolbox below it.
Closing a logbook¶
A logbook can be closed by clicking the Close Logbook button in the toolbar, or by clicking Close Logbook in the Logbook menu.